
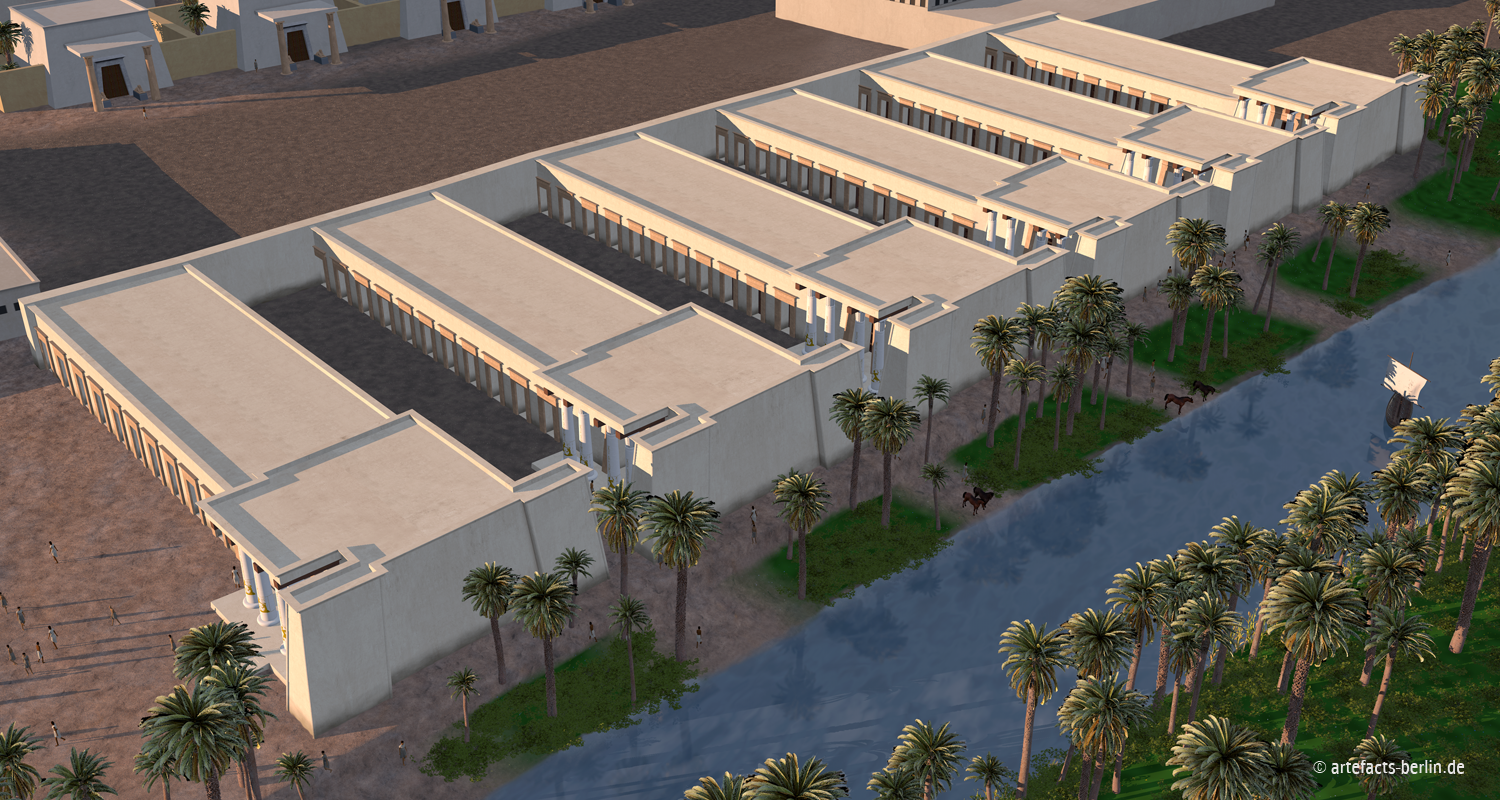
Recreation of PiRamses complex which held 300,000 inhabitants
What was in Pi-Ramses? Discovered by interpreting the data found from using Ground Penetrating Radar, Egyptologists believe that there was: Laid out on a Grid System of Roads and Canals, it has been referred to as the Egyptian Venice when the Nile Flood appeared each year At its centre was a substantial Temple.
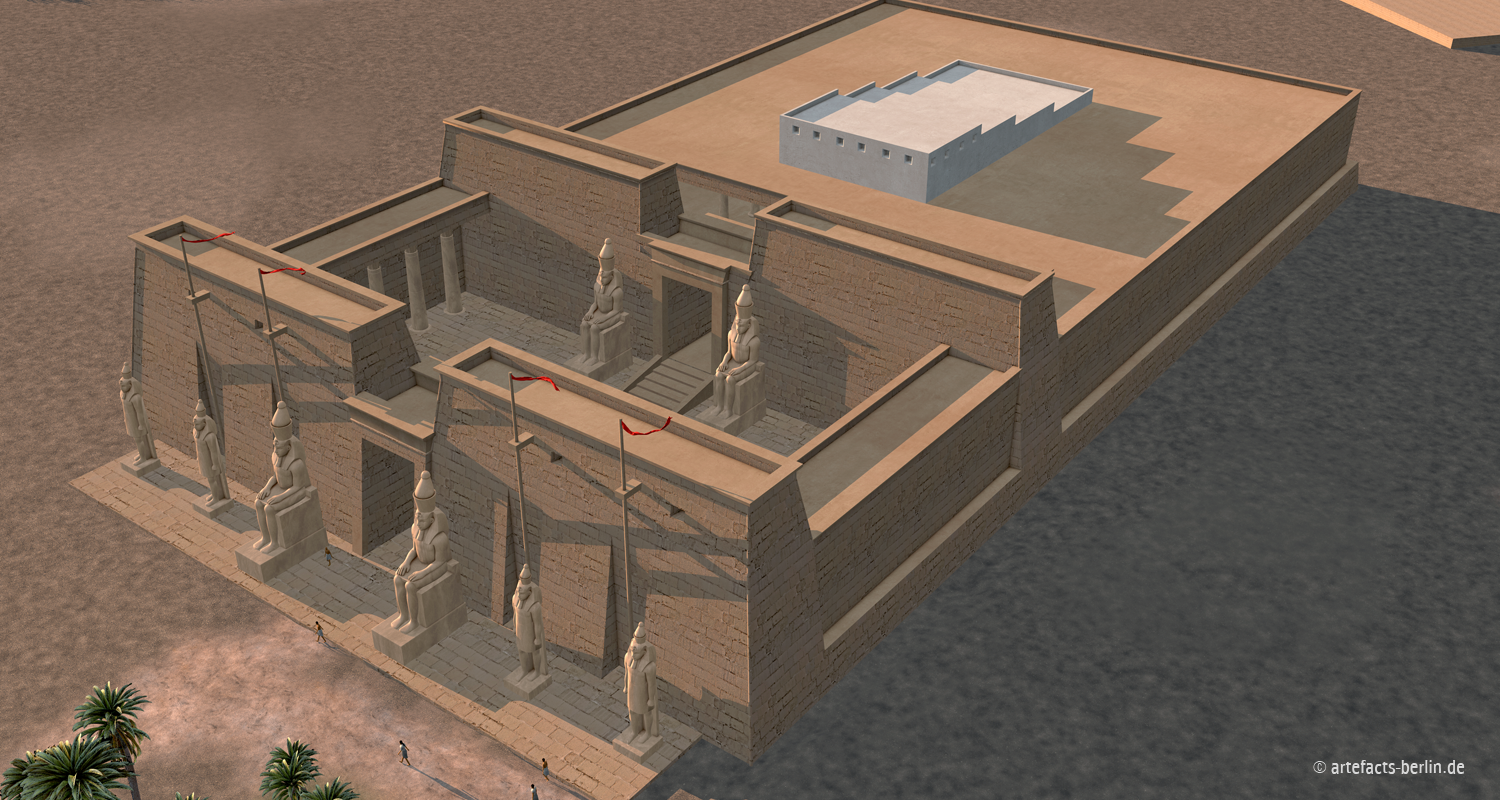

The reconstruction of PiRamesse Artefacts
Pi-Ramesse can without doubt be considered one of the most historically important cities of Ramesside Period Egypt and beyond. This article discusses the relationship between the physical and ideological reality of the Ramesside residence and the cultural and natural landscape which served as the base of the foundation of Pi-Ramesse.

PiRamesses Ramesses the Second
1275 BCE Per-Ramesses is functioning as a military-industrial center for launching campaigns from Lower Egypt . 1274 BCE Ramesses II launches his campaign against the Hittites at Kadesh from Per-Ramesses . c. 1069 BCE Per-Ramesses in decline as its harbors silt up and the New Kingdom of Egypt falls. c. 1060 BCE

Pi Ramesses Egypt
Pi-Ramesses was built on the banks of the Pelusiac branch of the Nile. With a population of over 300,000, it was one of the largest cities of ancient Egypt. Pi-Ramesses flourished for more than a century after Ramesses' death, and poems were written about its splendour.

Bible archeology City of Raamses Pi Ramesses Exodus 1 11 YouTube
Pi-Ramesses was the capital of Egypt under Ramesses II and the only city with the name "Ramesses" in the ancient world. Learn how it was founded, expanded, and abandoned by the Israelites, and how it relates to the Exodus story in Exodus 12:37 and Num 33:3-5.

PiRamsés Enciclopedia de la Historia del Mundo
Therefore, the name of Pi-Ramesses was only used during a specific slice of time during the later New Kingdom. This corresponds to four other Biblical names that can be found in 19th Dynasty texts: Pithom (as you mentioned), plus Succoth, Migdol, and Yam Suph, which is the equivalent of "pa-tufy" in the Anastasi III and VIII and the Onomasticon of Amenope.
Yan, Tan, Tethera Visit to Tanis 20.4.11
Pi-Ramesse, the capital of Ramesses II., is located in the Nile Delta of modern Egypt. This visualisation shows the structure and inner organisation of the city center and explains the reconstructive process. As this animation was created for an exhibition, there is no sound in this file. Please visit our website at: en.artefacts-berlin.de/.

PiRamesses Ancient History Encyclopedia
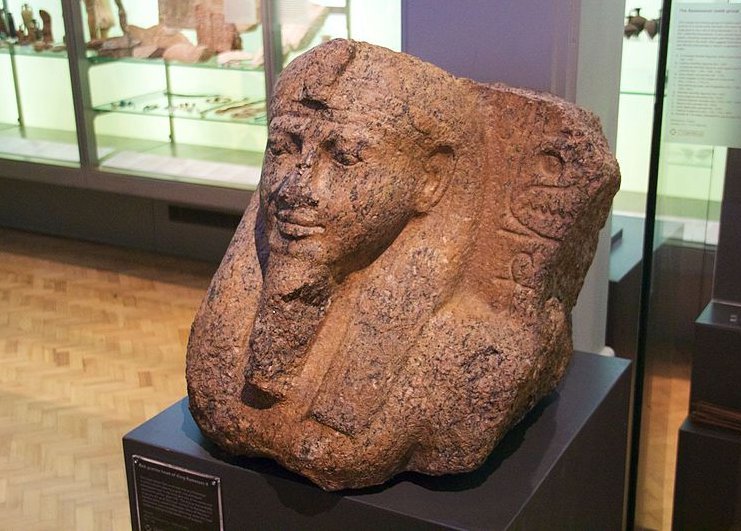
In 1941, the unveiling of a dozen royal Egyptian tombs at the ancient city of Tanis in the Nile Valley captured the imagination of archaeologists. French Egyptologist Pierre Montet's discoveries hinted at the possibility that Tanis might be the long-sought Pi-Ramesses. The site boasted granite blocks inscribed with the royal cartouche of.
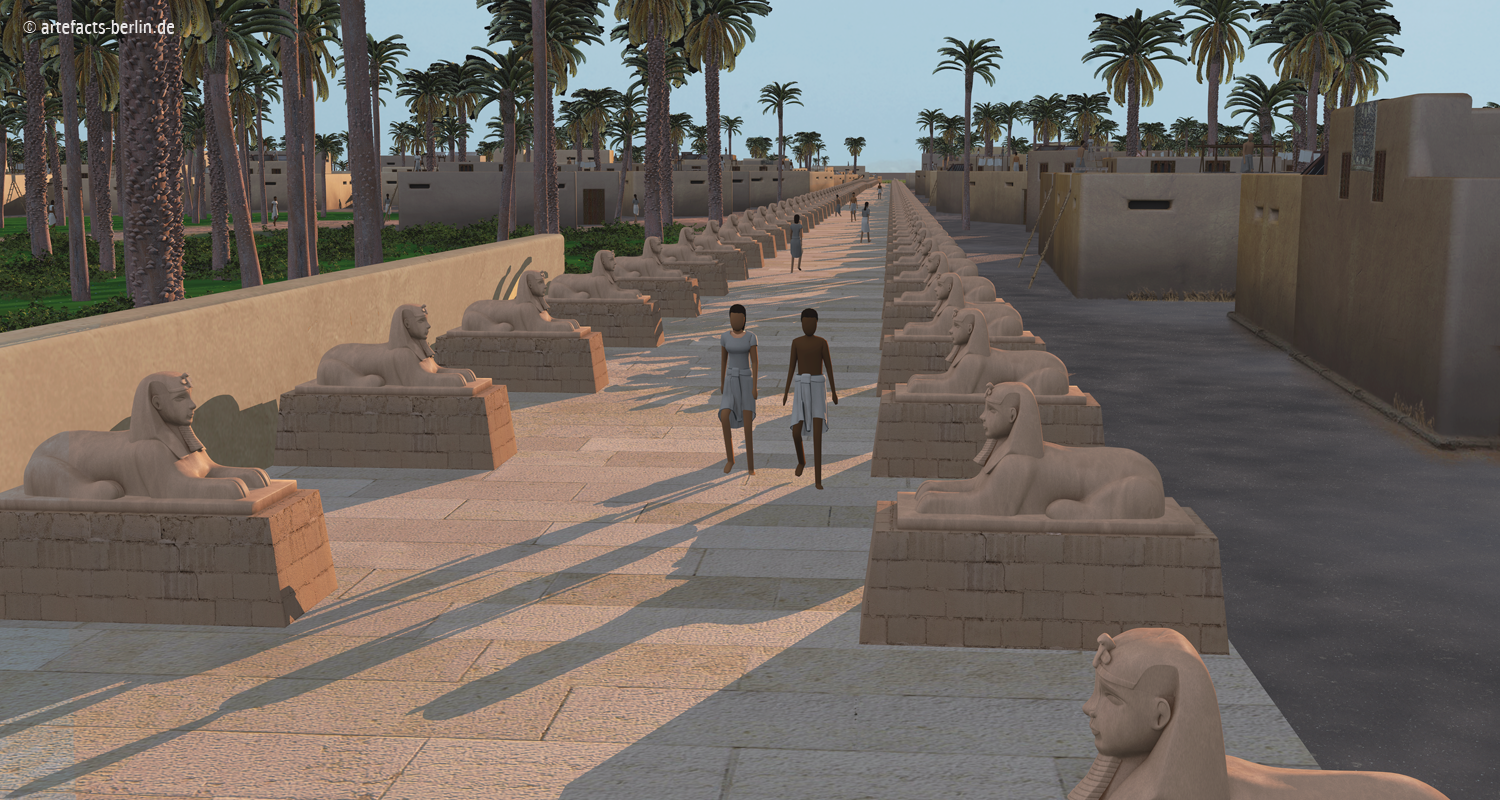

The reconstruction of PiRamesse Artefacts
Pi-Ramesses was an ancient Egyptian city built by the pharaoh Ramesses II of the 19th dynasty (also known as Ramesses the Great). It was located in the eastern delta of the Nile, near the modern city of Zagazig in Egypt.
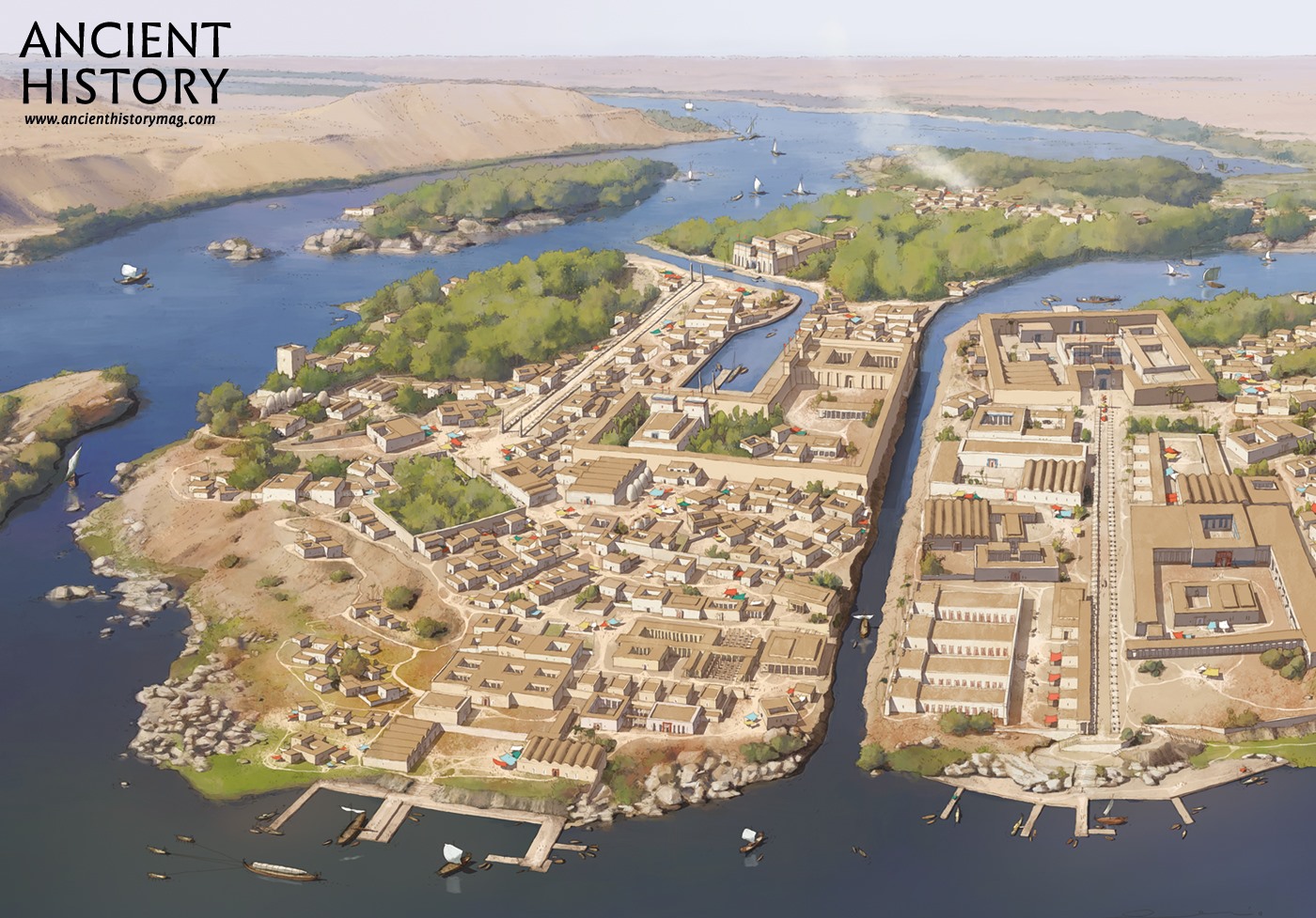

Reconstruction of PiRamesses (Illustration) World History Encyclopedia
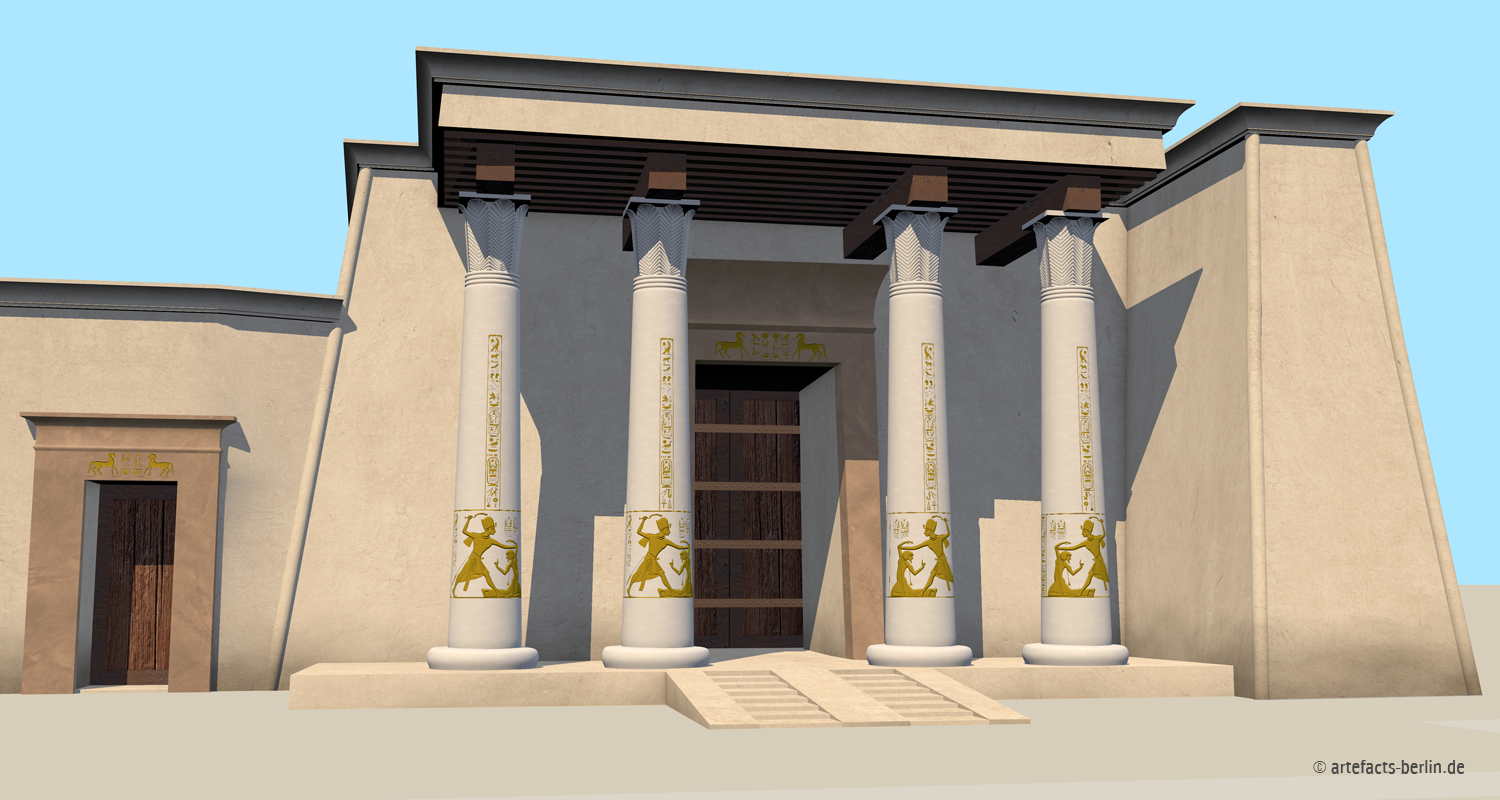
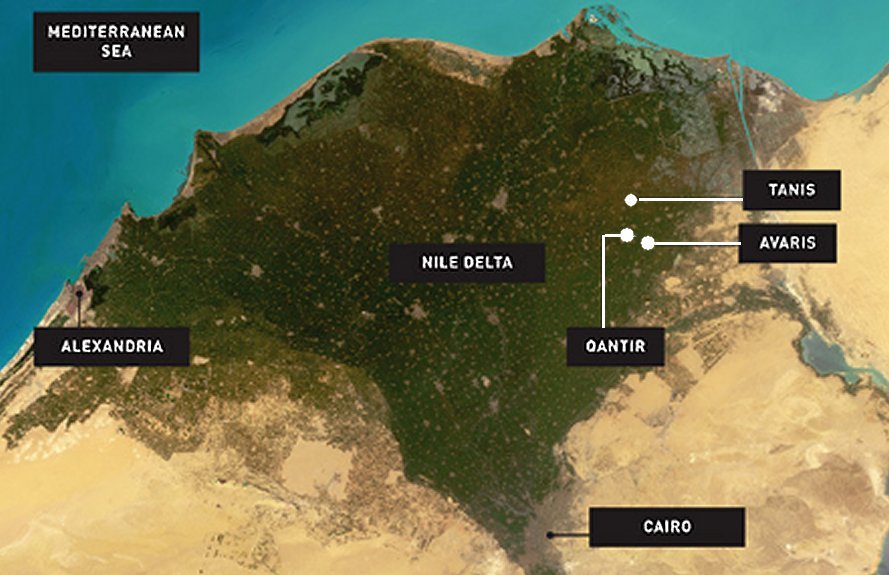
Qantir/Pi-Ramesse (House of Ramses) is situated in the Nile-Delta of Egypt, about 120 km northeast of Cairo. The city was founded by Ramesses II. in the 13th century BCE and was since then his main residence. It is structured by monumental palace and temple buildings and was the seat of the royal cariotry.

A reconstruction of PiRamesses in the 13th century BC, the new capital
Pi-Ramesses (also known as Per-Ramesses, Piramese, Pr-Rameses, Pir-Ramaseu) was the city built as the new capital in the Delta region of ancient Egypt by Ramesses II (known as The Great, 1279-1213 BCE). It was located at the site of the modern. Article by Joshua J. Mark Mummification in Ancient Egypt

The reconstruction of PiRamesse Artefacts
Reconstruction of the Egyptian capital of Pi-Ramesses, established by Ramesses II (1279-1213 BCE) in the 13th Century BCE. Illustration by Rocío Espin.

PiRamesse Pharaoh Ramesses II's Great Capital Surprisingly Identified
Pi- Ramesses (also known as Per-Ramesses, Piramese, Pr-Rameses, Pir-Ramaseu) was the city built as the new capital in the Delta region of ancient Egypt by Ramesses II (known as The Great, 1279-1213 BCE).

The reconstruction of PiRamesse Artefacts
Pi-Ramsès (ou Per-Ramsès), situé à l'emplacement de l'actuelle Qantir, fut la capitale de l' Égypte sous les XIXe et XXe dynastie s .
Yan, Tan, Tethera Visit to Tanis 20.4.11
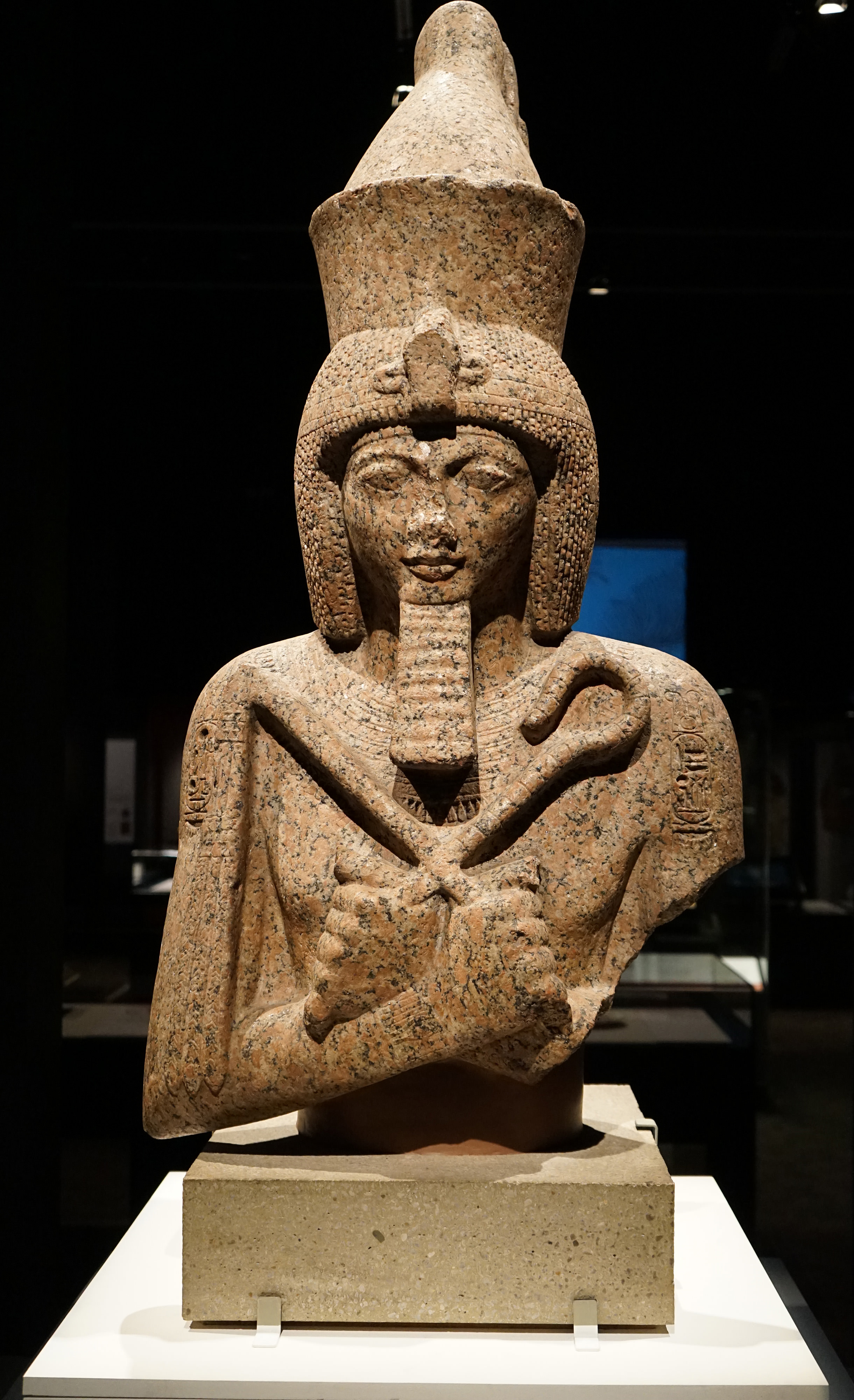
Map of Lower Egypt showing Tanis and Avaris, near Pi-Ramesses. (CC BY-SA 3.0) Ramesses II was a pharaoh who wanted to be remembered as the most influential Egyptian ruler. He adopted hundreds of monuments representing other pharaohs and ordered their names changed to his own. Therefore, many ancient statues identified previously as Ramesses II.
PiRamesse Pharaoh Ramesses II's Great Capital That Was Found In Two
Pi-Ramesses, the capital of Ramesses II., is located in the Nile Delta of modern Egypt. This visualization shows the structure and inner organization of the.